Google has become synonymous with searching for online information. Whether you’re looking for the latest news, a new recipe, or answers to your burning questions, Google is often the first place we turn to.
However, have you ever questioned how Google can provide such quick and relevant search results? The wonder of the world’s most popular search engine will be revealed as we explore the internal workings of Google step by step in this detailed guide.
Google’s search engine is a complex system that constantly scours the web for information and returns relevant results to users in a fraction of a second. It has evolved significantly since its inception in 1998, and today, it employs a sophisticated algorithm that considers hundreds of factors to determine the best search results for a given query. To understand how Google Search works, let’s break it down into several key steps.
Step 1: Web Crawling
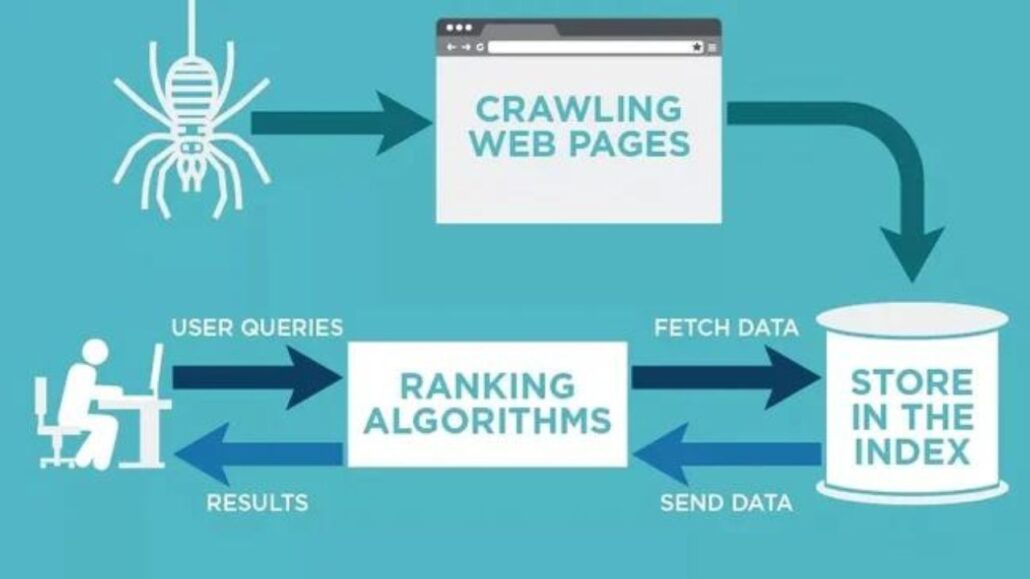
The first step in the Google Search process is web crawling. Google uses automated software programs called “spiders” or “crawlers” to visit websites online. These crawlers start their journey by visiting a few known websites and then follow links from one page to another. They use “URL discovery” to find new websites and pages to index.
When a crawler visits a webpage, it parses its HTML code to extract information about its content and structure. This information is then returned to Google’s servers, stored in a massive database called the “Google Index.”
Step 2: Indexing

Once the information from web pages is collected, it needs to be organized and stored efficiently so that Google can retrieve it quickly when a user performs a search. This is where the indexing process comes into play. Google’s index is like a vast library containing information about billions of web pages.
During indexing, Google’s algorithms analyze the content of web pages, including text, images, videos, and other multimedia elements. They also take note of various on-page factors such as keywords, headings, and metadata. This information is then catalogued in the index, making it searchable.
It’s important to note that Google’s index is not a static database but is constantly updated as new web pages are discovered and existing ones are updated. This ensures that search results are as up-to-date as possible.
Step 3: Ranking
Now that Google has a vast index of web pages, Finding the pages that are the most authoritative and relevant for a certain search query is the next stage. The renowned Google algorithm is used in this situation. Google uses a sophisticated algorithm to rank web pages, considering thousands of variables.
Some of the key factors that Google’s algorithm considers include:
Relevance
How well does a web page’s content match the search query? Pages with more relevant content are ranked higher.
Quality
Google evaluates the quality of the content and the website itself. High-quality content, reputable sources, and well-designed websites are given preference.
Authority
Google looks at how authoritative a website is in its respective niche. Websites with a strong track record and trustworthy websites with backlinks typically rank higher.
User Experience
Google considers factors like page load speed, mobile-friendliness, and overall user experience. Sites that provide a better user experience are favoured.
Freshness
For some queries, recency matters. Google may prioritize recently published or updated content for certain topics.
Geographic Relevance
For location-based queries, Google considers the user’s location and the geographic relevance of the content.
Step 4: Retrieval
When a user enters a search query, Google’s servers extract the most relevant results from the index. This involves matching the query to the indexed pages and ranking them based on the abovementioned factors.
Google doesn’t retrieve every page that matches a query; instead, it selects a subset of the websites most pertinent to the search query. This selection is made in milliseconds thanks to Google’s powerful infrastructure and algorithms.
Step 5: Displaying Results
After retrieving the most relevant results, Google formats them and displays them to the user. The search engine results page (SERP) typically consists of organic results, paid advertisements (if applicable), and features like featured snippets, knowledge panels, and related searches.
The primary listings that Google considers to be the best matches for the search are known as the organic results. They are ranked based on relevance and other factors, as discussed earlier.
Step 6: User Interaction
Google doesn’t stop at displaying search results. It also monitors how users interact with those results. User interaction data helps Google further refine its search algorithms and understand the quality of the results it provides.
Google tracks metrics like click-through rate (CTR), bounce rate, and dwell time. Bounce rate shows how frequently visitors leave the search results page without interacting with the clicked result, while CTR measures how frequently users click on a search result. The time a user spends on a page after clicking a result is measured by dwell time.
Step 7: Continuous Learning and Improvement
One of the reasons Google has remained the dominant search engine is its commitment to continuous learning and improvement. Google’s search engineers constantly refine and update the algorithm to provide users with better search results.
This process involves testing and experimenting with various changes to the algorithm, analyzing user feedback, and keeping up with the most recent changes in technology and web content. Google’s search team also fights against spam and manipulative tactics to maintain the integrity of its search results.
How Google Search Engine Works
Google Search Engine is a sophisticated web search platform that aims to retrieve relevant information quickly and accurately in response to user queries. It employs a vast index of web pages, continually updated through web crawling, to provide users with a comprehensive and up-to-date database.
When a user enters a search query, Google’s algorithms assess factors such as relevance, page quality, and user experience to deliver a ranked list of results. The search engine also considers the user’s location, search history, and personalized preferences to tailor results, enhancing the overall search experience.
How Google Search Engine Works Algorithm
The Google Search Engine Algorithm is the complex set of rules and processes that determine how the search engine interprets and ranks web pages in response to user queries.
Google utilizes a variety of algorithms, with the most notable being PageRank, which assesses the importance of web pages based on the quantity and quality of links. Over the years, Google has evolved its algorithms to include many factors: relevance, content quality, user experience, and mobile-friendliness.
The algorithm continuously learns and adapts, leveraging machine learning to improve search accuracy and stay ahead of evolving web content.
How a Search Engine Works
A search engine is a software application designed to retrieve information from the internet based on user queries. The process typically involves three main stages: crawling, indexing, and ranking.
In the crawling phase, the search engine uses automated bots (crawlers or spiders) to traverse the web, discovering and collecting information from web pages. The collected data is then indexed, creating a structured and searchable database. When a user submits a search query, the search engine’s ranking algorithm evaluates indexed pages to provide a list of results ranked by relevance.
Factors influencing ranking include keyword relevance, page quality, user engagement metrics, and other criteria specific to each search engine’s algorithm. The goal is to present users with the most relevant and reliable information based on their search intent.
Conclusion
The Google search engine is a complex and ever-evolving system that relies on intricate steps to deliver users the most relevant and useful results. Google’s search engine is a marvel of modern technology, from web crawling and indexing to ranking and user interaction monitoring.
Understanding how Google Search works step by step can provide valuable insights for website owners and digital marketers aiming to optimize their online presence. You may raise your chances of being prominently displayed in search results by producing high-quality, pertinent content and adhering to best practices. Google’s search results and reaching a wider audience on the world’s most popular search engine.
FAQ:
Google Search Explained?
What is the first step in the Google search process?
The first step is web crawling, where Google’s automated spiders or crawlers visit websites online to gather information.
What happens during the indexing process?
During indexing, Google analyzes the content of web pages, including text, images, and other elements, and stores this information in its massive database known as the Google Index.
How does Google’s algorithm determine the ranking of web pages?
Google’s algorithm considers hundreds of factors, including relevance, quality, authority, user experience, and more, to determine the ranking of web pages for a given search query.
How quickly does Google retrieve search results after entering a query?
Google’s powerful infrastructure lets it retrieve and display search results in milliseconds.
What is the search engine results page (SERP)?
The SERP page displays search results to users and typically includes organic results, paid advertisements, and features like featured snippets and knowledge panels.
What are organic search results?
Organic results are the main listings on the SERP that Google believes are the best matches for the user’s query. They are not paid advertisements.
How does Google track user interaction with search results?
To improve its search algorithms, Google monitors user interactions by monitoring click-through rate (CTR), bounce rate, and dwell duration.
How does Google work?
Google operates by crawling web pages, indexing content, and using sophisticated algorithms to rank results based on relevance and quality. User queries trigger the search engine to fetch and display the most pertinent information, ensuring efficient and accurate retrieval.
Why does Google constantly update its search algorithm?
Google updates its algorithm to provide users with better search results, adapt to changing web content, and combat spam and manipulative tactics.
Can website owners and digital marketers optimize their online presence for Google Search?
Yes, by creating high-quality, relevant content, following best practices for SEO (Search Engine Optimization), and staying updated with Google’s guidelines, website owners and marketers can improve their visibility in Google’s search results.
How does Google handle user privacy and data when conducting searches?
Google takes user privacy seriously and has measures to protect user data. It anonymizes personal information and allows users to control their privacy settings.
Can Google Search be accessed on mobile devices?
Yes, Google Search is accessible on mobile devices through web browsers and the Google Search app, providing a seamless search experience on smartphones and tablets.



