Master the Principles of Graphic Design, Graphic Design is a powerful tool that allows individuals and businesses to communicate visually in a creative and impactful way. Whether you’re a seasoned designer or just starting, mastering the principles of graphic Design is essential for creating stunning visuals that resonate with your audience.
What is Graphic Design?
Graphic Design is the art of combining text, images, and other visual elements to convey a message or idea. It encompasses various mediums, including print, digital, and multimedia.
Graphic Design is the art of visually communicating ideas and messages through the strategic arrangement of text, images, and other visual elements.
It involves creating designs that are not only visually appealing but also effectively convey a specific concept or message to the target audience.
Graphic designers utilize various design principles, typography, color theory, and layout techniques to create impactful visuals for mediums such as print, digital, and multimedia.
Importance of Graphic Design in Various Fields
Graphic Design plays a crucial role in branding, marketing, web design, product packaging, and more. It helps businesses establish their identity, communicate with their target audience, and differentiate themselves from competitors.
Graphic Design is highly important across diverse fields due to its ability to communicate ideas and messages effectively visually.
Whether in branding, marketing, web design, or product packaging, graphic design plays a pivotal role in conveying a brand’s identity, attracting target audiences, and differentiating businesses from competitors.
Its impact extends beyond traditional mediums to encompass digital platforms, making it an indispensable tool for modern communication and visual storytelling.
Design Principles
To create visually appealing designs, it’s essential to understand and apply fundamental design principles.
It was grasping the foundational concepts governing visual composition. It involves comprehending elements like balance, contrast, emphasis, and unity, which are crucial for creating aesthetically pleasing and effective designs across various mediums, from print to digital platforms.
Balance
Balance refers to the distribution of elements within a design. It can be symmetrical, asymmetrical, or radial, depending on the visual weight of each element.
Balance in Graphic Design refers to the strategic distribution of elements within a composition to create visual stability and harmony. Achieving balance involves carefully arranging elements such as text, images, and white space to ensure that no single element overwhelms the Design.
Whether symmetrical, asymmetrical, or radial, balance ensures that the overall composition feels cohesive and visually pleasing to the viewer.
Contrast
Contrast creates visual interest and emphasizes certain elements within a design. It can be achieved through variations in color, size, shape, texture, or typography.
The contrast in Graphic Design refers to the variation between elements, such as color, size, or shape, to create visual interest and emphasize certain aspects of a design.
By juxtaposing different elements, contrast helps to highlight important information and guide the viewer’s attention. It adds depth and dimension to the Design, making it more dynamic and engaging. Effective use of contrast enhances readability and creates a memorable visual impact.
Emphasis
Emphasis highlights the most important elements in a design, guiding the viewer’s attention and creating hierarchy.
Emphasis is a design principle that highlights key elements within a composition to draw attention and create hierarchy. It involves using techniques such as color, size, contrast, and placement to make certain elements stand out and convey importance.
By strategically applying emphasis, designers can guide the viewer’s eye and enhance the overall visual impact of their designs.
Unity
Unity brings harmony and coherence to a design by ensuring that all elements work together to convey a cohesive message or idea.
Unity in Graphic Design refers to the cohesive arrangement of elements within a composition. It ensures that all components work together harmoniously to convey a single message or idea.
By achieving unity, designers create visual coherence and clarity, enhancing the overall effectiveness of their designs. Through thoughtful placement and alignment, unity brings together disparate elements to form a cohesive and visually appealing whole.
Choosing the Right Color Palette
Color plays a significant role in graphic design, evoking emotions and conveying messages. Selecting the perfect color scheme is crucial in Graphic Design.
It involves strategically choosing colors that evoke the desired emotions and effectively convey the intended message. By understanding color psychology and harmonious color combinations, designers can create visually pleasing palettes that enhance the overall impact of their designs.
Whether aiming for contrast or harmony, choosing the right color palette sets the tone for successful visual communication.
Color Psychology
Different colors evoke different emotions and associations. Understanding color psychology can help designers choose the right colors to convey the desired message.
Color psychology explores how different colors affect human emotions, perceptions, and behaviors. It delves into the psychological impact of color on individuals and how it can influence mood, cognition, and decision-making processes.
By understanding color psychology, designers can strategically choose colors in their designs to evoke specific emotional responses or convey particular messages to their audience.
Harmonious Color Schemes
Harmonious color schemes, such as analogous, complementary, and triadic, create visually pleasing combinations that enhance the overall Design.
Harmonious color schemes are combinations of colors carefully selected to create a visually pleasing and balanced palette. These schemes utilize colors that complement each other, evoking a sense of unity and coherence in a design.
By incorporating harmonious color schemes, designers can enhance the overall aesthetic appeal of their creations while ensuring that the colors work together harmoniously to convey the intended message or evoke specific emotions.
Contrast and Accent Colors
Contrast and accent colors can be used to highlight important elements or create visual interest within a design.
The strategic use of hues that differ significantly from one another or the main color scheme. These colors are employed to create visual interest and emphasis within a design.
By juxtaposing contrasting colors or introducing accent hues, designers can draw attention to specific elements, enhance readability, and add depth to the overall composition, contributing to a dynamic and engaging visual experience.
Typography Essentials
Typography is the art of arranging type to make written language readable and appealing. Typography Essentials encompasses the fundamental aspects of type selection and arrangement in Graphic Design.
It involves choosing appropriate typefaces, pairing fonts effectively, and establishing hierarchy and readability within a design to enhance visual communication and appeal.
Typeface Selection
Choosing the right typeface is crucial for conveying the tone and personality of a design. It’s essential to consider factors such as readability, hierarchy, and brand identity.
Typeface selection involves choosing the appropriate font style for a design project. It plays a crucial role in conveying the intended tone and personality of the content.
By carefully selecting typefaces that align with the overall aesthetic and message, designers can enhance readability, establish hierarchy, and create a cohesive visual identity.
It’s essential to consider factors such as font style, weight, and readability to ensure effective communication with the target audience.
Font Pairing
Pairing fonts effectively can enhance the visual appeal of a design while maintaining readability and hierarchy.
Font pairing involves selecting and combining two or more typefaces to create visually harmonious and aesthetically pleasing text designs.
This process requires careful consideration of factors such as contrast, complementary styles, and overall readability to ensure that the chosen fonts complement each other effectively.
By pairing fonts strategically, designers can enhance the visual appeal and legibility of their designs while conveying the desired tone and message to the audience.
Hierarchy and Readability
Establishing hierarchy through font size, weight, and style helps guide the viewer’s eye and prioritize information within a design.
The arrangement of elements in a design creates a clear flow of information. It involves prioritizing content based on its importance and ensuring that text is easily legible for viewers.
This principle helps guide the viewer’s eye through the Design, ensuring that key messages are conveyed effectively. Proper hierarchy and readability are essential for creating visually appealing and easy-to-understand designs.
Composition Techniques
Composition refers to the arrangement of elements within a design to create a visually appealing and balanced layout.
Involves arranging design elements strategically to create visually appealing layouts. It encompasses principles like the rule of thirds, grid systems, and balance to achieve harmony and balance within a design, guiding the viewer’s eye effectively through the visual content.
Rule of Thirds
The rule of thirds divides the design space into a grid of nine equal parts, guiding the placement of key elements along the gridlines or intersections.
A fundamental composition technique in visual arts and photography involves dividing an image into nine equal parts using two horizontal and two vertical lines.
Important elements of the image are then placed along these lines or their intersections, creating a balanced and visually appealing composition. This technique helps draw the viewer’s eye to key points of interest and adds depth to the overall image.
Grid Systems
Grid systems provide a framework for organizing content and maintaining consistency across design elements.
Grid systems in graphic Design provide a structured framework for arranging elements within a layout. By dividing the design space into columns and rows, grid systems facilitate alignment, consistency, and organization.
They ensure that content is logically structured and visually appealing, enhancing readability and guiding the viewer’s eye through the Design.
Grid systems are essential for maintaining order and coherence in various design projects, from print materials to digital interfaces.
Symmetry vs. Asymmetry
Symmetrical compositions create a sense of balance and stability, while asymmetrical compositions can create a dynamic and visually interesting layout.
Symmetry vs. Asymmetry refers to comparing balanced, mirror-image arrangements and dynamic, unbalanced compositions in Design.
Symmetrical layouts offer a sense of stability and order through evenly distributed elements, while asymmetrical designs create visual interest and movement by positioning elements unevenly.
Understanding the nuances of both approaches allows designers to strategically choose the most suitable composition to convey their intended message or aesthetic.
Working with Shapes and Icons
Shapes and icons are essential graphic elements that can enhance a design’s visual appeal and functionality.
The art of integrating geometric forms and symbolic elements into your designs. Learn how to strategically use shapes and icons to enhance visual appeal, convey messages, and improve the user experience across various mediums.
Shapes in Design
Different shapes evoke different emotions and associations, and they can be used creatively to convey messages or ideas.
The pivotal role of geometric forms within visual compositions. It delves into how shapes influence the overall aesthetic and convey specific meanings or emotions to viewers.
Through deliberate manipulation of shapes, designers can create dynamic layouts that capture attention and communicate effectively.
Understanding the significance of shapes enhances the ability to craft compelling designs across various mediums, from print to digital platforms.
Iconography
Icons are simple, symbolic representations of objects, concepts, or actions. They are widely used in user interfaces and can enhance usability and communication.
The study or interpretation of visual symbols, icons, or images within a particular context, such as art, religion, or culture. It involves analyzing the meaning, significance, and historical context of these symbols to understand their cultural and artistic implications.
Iconography plays a crucial role in various fields, including art history, religious studies, and cultural anthropology, providing insights into the beliefs, values, and practices of different societies.
Space Effectively
Negative space, also known as white space, plays a crucial role in graphic Design by creating breathing room and emphasizing key elements.
It entails the strategic placement of elements to optimize design aesthetics and functionality. This involves utilizing negative space, aligning elements for cohesion, and prioritizing content to enhance the visual appeal and user experience within a given design framework.
Negative Space
Strategically using negative space can improve readability, create visual interest, and guide the viewer’s eye through the Design.
Negative space, often referred to as white space, is the unoccupied area surrounding the main elements in a design. It serves as a vital component in graphic compositions, providing balance, clarity, and visual breathing room.
By strategically incorporating negative space, designers can enhance the overall aesthetic appeal, improve readability, and draw attention to the focal points of the Design.
Proximity and Alignment
Grouping related elements through proximity and aligning them to a common axis creates a sense of unity and organization within a design.
Proximity and alignment in graphic Design refer to the strategic placement of elements in relation to each other and to the overall layout.
Proximity involves grouping related elements to create visual connections and establish hierarchy, while alignment ensures that elements are positioned in a way that creates a sense of order and cohesion.
These principles help improve readability, organization, and overall visual impact in design compositions.
Visual Hierarchy
Visual hierarchy is the arrangement of elements in a design to create a clear and organized flow of information.
Visual hierarchy comprehension involves arranging elements within a design to prioritize information effectively. It ensures that viewers are guided through the content logically, emphasizing key points and facilitating clear communication of the intended message.
Importance in Design
Establishing a visual hierarchy helps guide the viewer’s eye, prioritize information, and create a logical structure within a design.
Importance refers to the crucial role certain elements or principles play in creating effective visual communication. It encompasses factors like visual hierarchy, balance, and emphasis, which guide viewers’ attention and perception.
The importance of these elements allows designers to craft designs that are visually engaging, cohesive, and impactful, ultimately enhancing the overall effectiveness and clarity of the message being communicated.
Implementing Visual Hierarchy
Using techniques such as size, color, contrast, and spacing, designers can effectively establish visual hierarchy and improve the readability and impact of their designs.
Implementing visual hierarchy involves arranging design elements in a way that guides the viewer’s eye and emphasizes key information effectively.
It entails using techniques such as varying sizes, colors, contrasts, and spacing to create a clear and organized flow of information within a design.
By establishing a visual hierarchy, designers can ensure that important elements stand out and that the overall composition is visually appealing and easy to understand.
Incorporating Imagery
High-quality images, illustrations, and graphics can enhance the visual appeal and storytelling capabilities of a design.
Incorporating imagery involves strategically integrating high-quality visuals like photos, illustrations, and graphics into designs to enhance visual appeal and storytelling. It aims to engage audiences effectively through compelling visual elements.
High-Quality Images
Using high-resolution images that are relevant to the content can significantly improve the overall quality of a design.
High-quality images refer to visuals with superior resolution, clarity, and detail, enhancing the overall aesthetic and professionalism of a design or project.
These images are characterized by sharpness, accurate color representation, and minimal distortion, ensuring optimal visual impact and engagement.
High-quality images are essential in conveying messages effectively, capturing attention, and creating a visually appealing experience for viewers.
Illustrations and Graphics
Custom illustrations and graphics can add a unique and personal touch to a design, helping it stand out and communicate more effectively.
Illustrations and graphics are visual elements used in Design to enhance communication and engagement. They encompass a wide range of artistic styles and techniques, from hand-drawn illustrations to digital graphics.
These elements play a crucial role in conveying complex ideas, adding visual interest to content, and reinforcing brand identity. Whether it’s creating custom illustrations or incorporating pre-made graphics, they contribute significantly to the overall visual appeal and effectiveness of a design.
Enhancing User Experience
User-centered Design focuses on creating designs that are intuitive, accessible, and enjoyable for the end user.
Improving User Experience focuses on optimizing interactions between users and a product or service. It aims to enhance satisfaction by ensuring usability, accessibility, and overall enjoyment, ultimately leading to increased engagement and loyalty.
User-Centered Design
By understanding the needs, preferences, and behaviors of users, designers can create designs that are more user-friendly and effective.
User-centered Design prioritizes users’ needs and preferences throughout the design process. It focuses on creating products and experiences that are intuitive, accessible, and enjoyable for the end user.
By understanding user behavior and incorporating their feedback, User-Centered Design ensures that designs meet the requirements and expectations of the target audience, ultimately leading to improved usability and satisfaction.
Accessibility Considerations
Designing with accessibility in mind ensures that everyone, regardless of ability, can access and interact with the design content.
The practice of ensuring that digital content, websites, and applications are usable and accessible to all individuals, including those with disabilities.
It involves implementing design features and functionalities that accommodate diverse needs, such as screen reader compatibility, keyboard navigation, and color contrast adjustments.
By prioritizing accessibility, developers and designers create inclusive experiences that enable everyone to access and interact with digital content effectively.
Software Tools for Graphic Design
Master the Principles of Graphic Design, Various software tools are available to assist designers in creating and editing visual content. Graphic design software tools are essential for creating visual content.
Popular options like Adobe Suite, Canva, and Sketch offer diverse features for editing images, designing layouts, and enhancing creativity in both digital and print projects.
Adobe Suite (Photoshop, Illustrator, InDesign)
Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, and InDesign are industry-standard software tools used for graphic Design, photo editing, and desktop publishing, respectively.
The Adobe Suite, comprising Photoshop, Illustrator, and InDesign, is a comprehensive set of industry-standard software tools for graphic Design, photo editing, and desktop publishing.
Photoshop is renowned for image manipulation and retouching, while Illustrator excels in vector-based artwork creation. InDesign is widely used for layout design, including publications like magazines and brochures. Together, these applications empower designers to create professional-grade visuals and publications efficiently.
Canva
Canva is a user-friendly online design tool that offers a wide range of templates, graphics, and editing features for creating professional-looking designs.
Canva is a user-friendly online design platform that offers a wide range of templates and editing features for creating professional-looking graphics and documents.
With its intuitive interface and extensive library of design elements, Canva is a popular choice for individuals and businesses looking to create visually appealing content without the need for advanced design skills.
Sketch
Sketch is a popular design tool among UI/UX designers. It is known for its intuitive interface and powerful vector editing capabilities.
Sketch is a versatile graphic design software renowned for its intuitive interface and robust vector editing capabilities.
It offers a comprehensive set of tools tailored for UI/UX designers, enabling seamless creation of prototypes, wireframes, and high-fidelity designs.
With features like symbol libraries, artboards, and a responsive layout system, Sketch empowers designers to efficiently translate ideas into visually stunning digital experiences.
Designing for Different Platforms
Master the Principles of Graphic Design, Design considerations vary depending on the platform and medium in which the design will be displayed.
It involves adapting visual content to suit various mediums, such as websites, print materials, and social media. It requires considering factors such as screen size, resolution, and platform-specific guidelines to ensure optimal user experience and engagement.
Web Design
Web design focuses on creating visually appealing and functional websites that provide a seamless user experience across different devices and screen sizes.
Web design involves the creation and arrangement of visual elements, layout, and functionality for websites.
It encompasses various aspects such as graphic Design, user interface design, and user experience design to ensure a seamless and engaging online experience for visitors.
Web designers utilize coding languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, along with design software, to craft aesthetically pleasing and user-friendly websites tailored to meet specific business goals and user needs.
Print Design
Print design involves creating designs for physical materials such as business cards, brochures, posters, and packaging, taking into account factors such as size, resolution, and printing specifications.
Print design involves creating visual materials for physical distribution or display, such as brochures, posters, business cards, and packaging.
It focuses on designing content that will be printed on tangible surfaces, considering factors like layout, color, typography, and printing specifications.
Print design aims to create visually appealing and impactful materials that effectively communicate messages and engage audiences in various offline contexts.
Social Media Graphics
Designing graphics for social media requires an understanding of platform-specific guidelines, image dimensions, and best practices for engaging with the target audience.
Social media graphics are visual elements specifically tailored for platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and LinkedIn.
They include images, infographics, and illustrations designed to engage audiences and convey messages effectively within the constraints of social media platforms.
These graphics play a crucial role in enhancing brand visibility, driving engagement, and conveying information in a visually appealing manner across various social media channels.
Staying Updated with Trends
Master the Principles of Graphic Design, Graphic design trends evolve constantly, influenced by technological advancements, cultural shifts, and aesthetic preferences.
Keeping abreast of current trends in graphic design ensures relevance and creativity in your work. By staying updated, you can incorporate fresh ideas and techniques, enhance the visual impact of your designs, and stay competitive in the field.
Current Design Trends
Staying informed about current design trends can inspire creativity and help designers stay relevant in a rapidly changing industry.
The prevailing styles, techniques, and visual elements are popular in the field of graphic design at present. It encompasses the latest innovations, aesthetic preferences, and creative approaches that designers are incorporating into their work.
Staying informed about current design trends is essential for designers to remain relevant and to create visually compelling and engaging designs that resonate with their target audience.
Incorporating Trends Wisely
While staying updated with trends is essential, it’s equally important to incorporate them thoughtfully and in a way that aligns with the brand identity and objectives.
Integrating current design trends into your work with thoughtful consideration ensures they align harmoniously with your brand identity and objectives.
This approach involves discerning which trends are relevant and beneficial for achieving your design goals while avoiding overuse or dilution of your unique visual style.
Case Studies of Successful Designs
Master the Principles of Graphic Design, Analyzing real-life examples of successful designs can provide valuable insights and inspiration for aspiring designers.
Analyzing Effective Designs
Master the Principles of Graphic Design, By deconstructing and analyzing successful designs, designers can learn valuable lessons about composition, typography, color usage, and overall visual communication.
Involves dissecting visually appealing and well-executed graphic designs to understand their key elements and strategies.
This process helps designers gain insights into effective composition, color usage, typography, and overall visual communication.
By studying successful designs, designers can enhance their skills and techniques to create impactful and engaging visuals.
Learning from Real-Life Examples
Master the Principles of Graphic Design, Examining case studies of successful design projects can help designers understand the decision-making process, challenges faced, and strategies employed to achieve the desired outcomes.
They were drawing insights from actual scenarios or practical instances to gain valuable knowledge and inspiration.
By examining real-life cases, individuals can understand the practical application of concepts and strategies, enhancing their learning experience.
Real-life examples offer tangible evidence and context, facilitating a deeper understanding of principles and their implications in various situations.
It provides a hands-on approach to learning, enabling individuals to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios effectively.

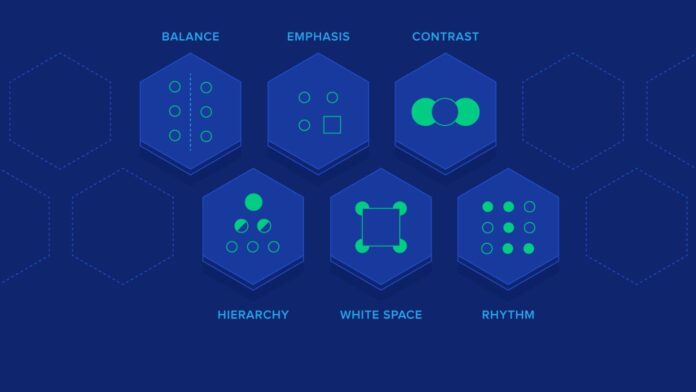
7 Main Principles of Graphic Design
Master the Principles of Graphic Design, Encompass fundamental guidelines for effective visual communication. These principles include balance, hierarchy, contrast, proportion and scale, emphasis, repetition, and proximity, each playing a vital role in creating harmonious and impactful designs.
1. Balance
Balance in Graphic Design involves the equal distribution of visual weight within a composition, creating stability and harmony. It can be achieved through symmetrical arrangements where elements are mirrored on both sides of a central axis or asymmetrical compositions where various elements are balanced based on their size, color, or visual importance. Maintaining balance ensures that the Design feels cohesive and visually pleasing to the viewer.
2. Hierarchy
Hierarchy establishes the importance of elements within a design, guiding the viewer’s focus. It organizes content based on significance, ensuring clarity and ease of understanding. By prioritizing certain elements over others, hierarchy creates a structured visual flow, facilitating effective communication. Through variations in size, position, and style, elements are arranged in a deliberate order, leading the viewer’s eye through the Design logically.
3. Contrast
The contrast in Graphic Design entails the deliberate variation of visual elements like color, size, or shape to create striking differences. This technique enhances visual interest and highlights important aspects of a composition. By juxtaposing different elements, contrast helps draw attention, establish hierarchy, and improve readability. Whether through light and dark shades, bold and subtle colors, or large and small objects, contrast adds depth and dynamism to designs, making them more engaging and effective.
4. Proportion and scale
Proportion and scale in graphic Design entail managing the relative sizes and ratios of elements within a composition. Properly adjusting these aspects fosters harmony and coherence in the overall layout. Scale, on the other hand, allows designers to emphasize specific elements or create a visual hierarchy by adjusting their sizes accordingly. Both proportion and scale play crucial roles in guiding viewer perception and understanding of the Design’s message.
5. Emphasis
Emphasis on graphic Design highlights key elements to draw viewers’ attention. Achieved through various techniques like contrast, color, and size, it ensures important information stands out amidst other elements. By strategically emphasizing, designers guide the viewer’s focus, creating hierarchy and clarity within the composition. It plays a crucial role in communication, directing the viewer’s gaze and reinforcing the intended message or purpose of the Design.
6. Repetition
Repetition in graphic Design involves the consistent use of certain elements or patterns throughout a design. By repeating elements like shapes, colors, or motifs, designers create unity and establish a visual rhythm. This repetition reinforces the overall message, enhances readability, and adds visual interest. It helps to guide the viewer’s eye through the Design, creating a cohesive and harmonious composition.
7. Proximity
Proximity in Graphic Design refers to the arrangement of elements with each other. By placing related items close together, designers create visual connections and convey relationships. This principle helps organize information effectively, guiding the viewer’s understanding of the content. Grouping elements based on their relevance or association enhances clarity and readability, facilitating easier interpretation of the Design.
Elements of Graphic Design
Master the Principles of Graphic Design, Graphic design elements serve as the foundational components that designers utilize to craft compelling visual compositions. These elements encompass:
- Line: Serving as the fundamental building block, lines come in various forms—straight, curved, diagonal, or organic. They imbue the Design with a sense of direction, movement, and structure.
- Shape: Shapes, whether geometric or organic, delineate objects or delineate areas within the Design. Ranging from simple circles and squares to intricate abstract forms, they contribute to the overall visual appeal.
- Color: Harnessing hues, tints, and shades, color evokes emotions, sets the mood, and leaves a lasting visual impact. It serves as a potent tool for grabbing attention and solidifying brand identity.
- Texture: Whether tangible or visually implied, texture refers to the tactile quality or appearance of surfaces within the Design. It injects depth and visual intrigue into the composition.
- Typography: The art of arranging and utilizing fonts in an aesthetically pleasing manner. Typography is pivotal in conveying information effectively and eliciting desired emotional responses.
- Space: The area or distance between elements within the Design. Strategic utilization of space fosters balance guides the viewer’s gaze and accentuates key elements.
- Value: The degree of lightness or darkness exhibited by an element within the Design. Value aids in creating contrast, depth, and the illusion of three-dimensionality.
Conclusion
Master the Principles of Graphic Design, Mastering the principles of graphic design requires a combination of technical skills, creativity, and an understanding of design theory. By applying fundamental principles such as balance, contrast, typography, and composition, designers can create stunning visuals that effectively communicate messages and engage audiences.
FAQ
How Do You Master Design Principles?
Master the Principles of Graphic Design, To master design principles:
- Study fundamental concepts like balance, contrast, emphasis, and rhythm.
- Analyze existing designs, seek feedback, and practice regularly.
- Experiment with different styles and mediums, and strive for both creativity and functionality in your work.
How Do You Make Graphics Stunning?
Master the Principles of Graphic Design, Create stunning graphics, focus on vibrant colors, sharp details, and dynamic compositions. Utilize lighting and shadow effects to add depth. Experiment with textures and layers for richness. Pay attention to balance and contrast to captivate the viewer’s attention.
How Do I Learn Graphic Design Principles?
Master the Principles of Graphic Design, Learn graphic design principles, study composition, typography, color theory, and visual hierarchy, analyze design examples to understand how they effectively communicate messages, practice by creating your designs, and seek feedback to refine your skills. Online tutorials and courses can also be valuable resources.
How Do You Master Graphic Design?
Master the Principles of Graphic Design, Mastering Graphic Design requires studying design principles, practicing various software tools, and exploring typography, color theory, and composition. Stay updated with industry trends, seek feedback, and experiment creatively. Continuously refine skills, adapt to new technologies, and cultivate a unique design style through dedication and perseverance.
What are the 7 Basic Graphic Design Principles?
Master the Principles of Graphic Design, The 7 basic graphic design principles are balance, alignment, contrast, repetition, proximity, hierarchy, and space. These principles guide the arrangement and presentation of elements in Design to create visually appealing and effective communication.
What are the 12 Rules of Graphic Design?
- Align elements purposefully.
- Maintain consistency in typography.
- Use contrasting colors for emphasis.
- Employ whitespace strategically.
- Ensure readability with appropriate font sizes.
- Simplify complex ideas visually.
- Balance elements harmoniously.
- Respect grids for the organization.
- Prioritize clarity over ornamentation.
- Embrace simplicity in Design.
- Create a visual hierarchy for clarity.
- Pay attention to details.



Its like you read my mind! You appear to know so much about this,
like you wrote the book in it or something. I think that you can do with
a few pics to drive the message home a little bit,
but other than that, this is great blog. A fantastic read.
I’ll certainly be back.